Launching a software-as-a-service, or SaaS, product is only half the battle. The real challenge lies in bringing it to market effectively, winning users, and building predictable growth. A Go-To-Market, or GTM, strategy gives structure to that process. It’s the blueprint for how your SaaS company identifies customers, communicates value, and scales revenue over time.
But, building a scalable GTM strategy requires a thoughtful combination of research, positioning, pricing, technology, and repeatable tactics that can evolve as your business grows. Keep reading to learn everything you need to know about building a successful GTM strategy.
Understanding the Foundation of a GTM Strategy
Before diving into specific tactics, it’s important to define what a GTM strategy actually includes. For SaaS companies, it’s the overall plan for how to reach target customers, communicate value, and convert leads into loyal users. A successful GTM plan connects marketing, sales, product, and customer success into one unified approach. It ensures everyone works toward the same growth goals. Without that alignment, teams risk chasing different metrics, confusing prospects, and losing momentum.
A GTM strategy helps answer key questions. Who are you selling to? What problems are you solving? Why should customers choose you? And how will you consistently reach and convert them?
Step 1: Define Your Ideal Customer Profile (ICP)
Every scalable GTM strategy starts with clarity around your audience. SaaS products are built to solve specific problems, but without understanding who experiences those problems most acutely, marketing efforts will lack focus. An Ideal Customer Profile, or ICP, goes beyond simple demographics. It defines the characteristics of companies or individuals that get the most value from your product and are most likely to become long-term customers. For B2B SaaS, this may include industry, company size, tech stack, and business challenges.
Once your ICP is clear, everything from your messaging to your channel strategy becomes more efficient. This will help you build campaigns that resonate, tailor sales conversations, and prioritize leads that actually fit your target audience.

Step 2: Craft a Strong Value Proposition
Your value proposition is the promise that connects your product to your customer’s needs. It explains how your SaaS solution makes their life easier, saves time, or drives measurable results. A common mistake among SaaS companies is focusing too much on product features rather than outcomes. Customers don’t care about every function your software performs; they care about what those functions achieve for them.
To build a scalable GTM strategy, your value proposition should be simple, specific, and rooted in your ICP’s most pressing problems. Conduct interviews, analyze customer reviews, and use tools like Typeform or Hotjar to collect feedback directly from users. As a result, the clearer you are about the benefits customers receive, the more persuasive your messaging becomes across all channels.
Step 3: Positioning and Differentiation
standing out is essential. Positioning defines where your product fits compared to competitors and how you want it to be perceived. Start by analyzing your competitors’ messaging, pricing, and features. Identify what they emphasize, and where they fall short. Your differentiation might be based on ease of use, customer support, integrations, or unique functionality.
A helpful framework is the “Jobs to Be Done” model, which focuses on what customers are “hiring” your software to do. Understanding the job your product performs gives you the foundation to position it clearly. For example, rather than promoting a generic CRM tool, a SaaS company could position itself as “the CRM built specifically for small marketing agencies.” This level of clarity attracts the right audience and filters out poor-fit leads, saving marketing and sales teams time as you scale.
Step 4: Choose the Right GTM Model
Your GTM model is the approach you’ll use to bring your product to market and acquire customers. In SaaS, three primary models tend to work best depending on your pricing and target audience.
A sales-led model relies heavily on direct sales efforts. This approach works well for enterprise SaaS solutions with higher price points and longer sales cycles.
A product-led model focuses on letting the product sell itself. Think of companies like Slack or Dropbox, where users can try the product for free and upgrade later. This model emphasizes user experience, onboarding, and self-service features.
A marketing-led model places demand generation at the forefront. It’s built around content, advertising, and inbound strategies that drive sign-ups and nurture leads at scale.
Many SaaS companies combine these models as they grow. Early-stage companies might rely on product-led tactics to gain traction, then layer in a sales team as larger clients come on board. The key is to choose a model that aligns with your customer’s buying behavior and your team’s strengths.

Step 5: Build the Right Tech Stack
To scale efficiently, SaaS companies need a tech stack that supports every part of the GTM strategy. The right tools can automate manual work, track results, and provide insights that drive smarter decisions.
Your stack will depend on your GTM model, but typically includes CRM, marketing automation, analytics, customer support, and communication tools.
For example, a strong foundation might include:
- HubSpot or Salesforce for CRM and marketing automation
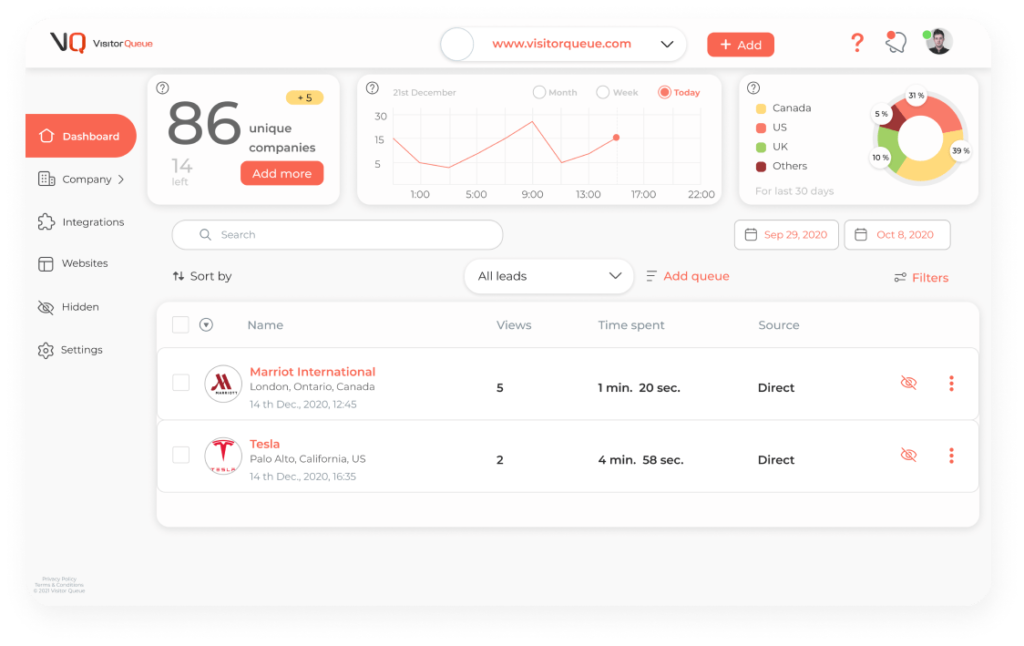
- Visitor Queue for identifying website visitors and intent data
- Google Analytics for performance tracking
- Zendesk for customer engagement and support
- Slack for internal collaboration
What matters most is integration. The tools you choose should communicate with each other to create a unified view of your customer journey. When marketing, sales, and support share data, scaling becomes significantly easier.
Step 6: Develop a Content Strategy That Educates and Converts
Content marketing remains one of the most effective and scalable ways to attract and nurture leads for SaaS companies. But not all content is created equal. To support a GTM strategy, content needs to align with every stage of the buyer journey, from awareness to decision.
In the awareness stage, focus on educational blog posts, industry guides, and webinars that address pain points. At the consideration stage, create comparison pages, case studies, and whitepapers that show how your solution stacks up. At the decision stage, use testimonials, pricing pages, and free trials to remove friction.
Tools like SEMrush can help identify keywords your audience is searching for. Combined with Google Search Console, these tools reveal what’s working and where to improve. As your company grows, building a scalable content strategy means repurposing content across channels. Turn blog posts into LinkedIn articles, short videos, and email series. As a result, this multiplies your reach without multiplying effort.
Step 7: Invest in Data-Driven Marketing and Demand Generation
A scalable GTM strategy relies on predictable lead flow, which comes from consistent demand generation. Paid ads, SEO, and partnerships all contribute, but the key is measurement and iteration. Start by defining clear marketing goals tied to revenue. This could include marketing qualified leads (MQLs) or cost per acquisition (CPA). Use analytics tools to measure what’s driving results and where leads drop off in the funnel.
Visitor Queue can help by identifying which companies visit your website and what pages they interact with. This information allows your sales team to reach out to warm leads before competitors do. Demand generation should also include email nurturing, remarketing, and retargeting campaigns. Marketing automation tools like HubSpot or Marketo make it easy to build scalable workflows that keep prospects engaged over time.
Step 8: Build a Sales Process That Scales
Even with a great product and marketing strategy, growth will stall without a clear sales process. For SaaS companies, scalability comes from repeatability, every rep should follow the same playbook for prospecting, demos, and closing deals. Document your sales stages and define clear handoff points between marketing and sales. Use CRM automation to track progress and identify where deals get stuck. As you scale, consider implementing sales enablement tools like SalesLoft or Gong to improve communication and analyze performance. For smaller SaaS businesses or product-led companies, self-service models with built-in onboarding flows can reduce the need for manual sales support. This allows you to grow faster without expanding the sales team at the same rate as revenue.
Step 9: Retention and Customer Success as Growth Drivers
One of the most overlooked parts of a GTM strategy is customer success. In SaaS, recurring revenue depends on keeping customers engaged and reducing churn. A scalable GTM plan must include retention strategies that turn users into advocates. Start by setting up an onboarding process that ensures users understand how to get value quickly. Follow up with personalized check-ins and helpful resources to keep customers active. Monitor engagement metrics such as daily active users or feature adoption rates. If these numbers start to drop, customer success teams can proactively reach out before cancellations occur. Retention also ties into expansion revenue. Happy customers are more likely to upgrade or refer others. Incorporating upsell campaigns and referral programs into your GTM plan creates an additional growth channel that scales efficiently.
Step 10: Use Feedback Loops to Improve Over Time
A scalable GTM strategy isn’t a one-time project. It evolves as you gather data, test new ideas, and respond to customer feedback. Implement regular check-ins between marketing, sales, and customer success teams to share insights. What messages resonate most? Which campaigns drive the highest-quality leads? What do customers mention in support tickets or NPS surveys? Tools like Notion or Asana can help track feedback and assign action items. When feedback turns into real changes, whether to messaging, pricing, or product features, your GTM strategy naturally strengthens over time.
Step 11: Pricing Strategy That Supports Growth
Pricing is one of the most important parts of any SaaS GTM plan. It affects how customers perceive your value, who you attract, and how fast you grow. SaaS companies often choose between tiered pricing, usage-based pricing, or freemium models. Tiered pricing allows you to serve multiple market segments, while usage-based pricing aligns cost with customer value. Freemium models work well in product-led growth by lowering the barrier to entry. A scalable pricing model grows with your customer. It encourages upgrades rather than churn and ensures long-term profitability.
Step 12: Align Teams Around Shared Metrics
Scalability depends on cross-functional alignment. When marketing, sales, product, and customer success share goals and metrics, the entire organization moves in the same direction. Define shared KPIs such as customer acquisition cost (CAC), lifetime value (LTV), and conversion rates. When everyone understands how their work impacts revenue and retention, collaboration improves naturally. That alignment is what turns a good GTM strategy into a scalable one.
Step 13: Testing, Iteration, and Continuous Optimization
No GTM strategy is perfect from the start. SaaS companies that scale successfully view experimentation as part of their culture. A/B test your messaging, landing pages, and onboarding flows. Try new pricing tiers or different CTAs in your ads. Measure results and use insights to refine your approach. This process doesn’t just optimize conversion rates, it also uncovers what resonates most with customers. The more you test and learn, the faster your GTM strategy compounds into long-term growth.
Final Thoughts: Building for Scale, Not Just Launch
A strong GTM strategy is what takes a great SaaS product into a thriving business. It connects every department, keeps messaging consistent, and builds momentum that compounds over time. Scalability doesn’t mean doing more, it means doing what works, repeatedly and efficiently. With a clear ICP, compelling value proposition, the right tools, and alignment across teams, your GTM strategy can grow alongside your product. If you have any questions about how Visitor Queue can be used to identify your website visitors, do not hesitate to reach out.
 Identify
Identify Personalize
Personalize Benchmark
Benchmark Agencies
Agencies Integrations
Integrations Case Studies
Case Studies Use Cases
Use Cases Blog
Blog Resources
Resources